In modern electronic components devices, we find a single component that is the core of the effort: the circuit board, or printed circuit boards (PCBs). Boards of this variety range from smartphones to household appliances, which ensure the proper functioning of electric circuits by providing the necessary processing ability that connects the components together while holding them in place. Specifying the alteration of various components that make up the circuit board is thus a necessity for anyone who is sailing in the electronics realm, whether a student, player, or worker as well. This guide is intended to address misapprehensions about the working principles of the interior workings of a typical circuit board as it explains the various components and their functions.
What is a PCB component?
A PCB (Printed Circuit Board) component is any electronic components part that is going to be mounted on a circuit board, including resistors, capacitors, transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits. These parts are the ones that are attached to the PCB and do very important tasks like amplifying signals, storing energy, processing data, and performing many other critical functions.
Printed circuit board Components Identification
Recognizing the various parts of a printed circuit board (PCB) becomes quite essential in repair, troubleshooting, and studying electronic gadgets. Here’s a basic guide to help you recognize common PCB components:
Resistors
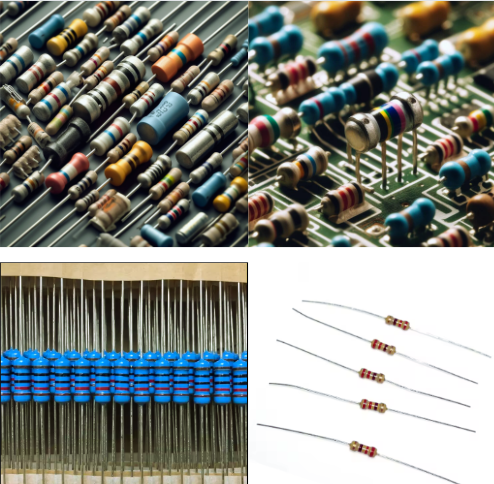
- Appearance: It’s usually found in solid form, and it’s shape resembles a tube. Its color graduation (from one band to the other) helps you tell the resistance level.
- Function: inhibit the movement of electric charge, decrease potential, and lessen the current.
2. Capacitors
- Appearance: They assure possess a common nature, the two kinds being cylindrical capacitors and small and flat ceramic disks.
- Function: Utilize a store of electrical signal energy temporarily to serve in filtering, buffering, and signaling functionalities.
3. Inductors
- Appearance: Wire in spiral form and magnetic cores are often used.
- Function: Use a magnetic field for storing energy when electric current runs through; jelly filters and oscillators are some of the appliances they are included in.
4. Diodes
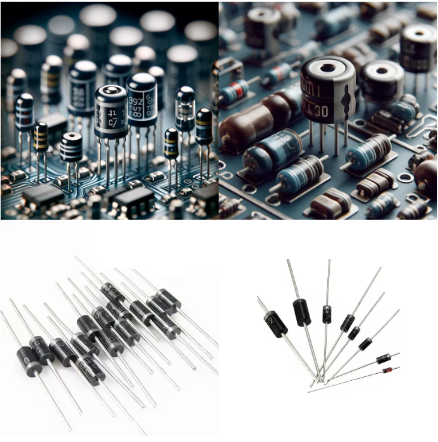
- Appearance: There are small components with a chopped line that indicates the anode; the packages, on the other hand, vary.
- Function: Permits current to go only in one direction and, consequently, can be used as rectifiers.
5. Transistors
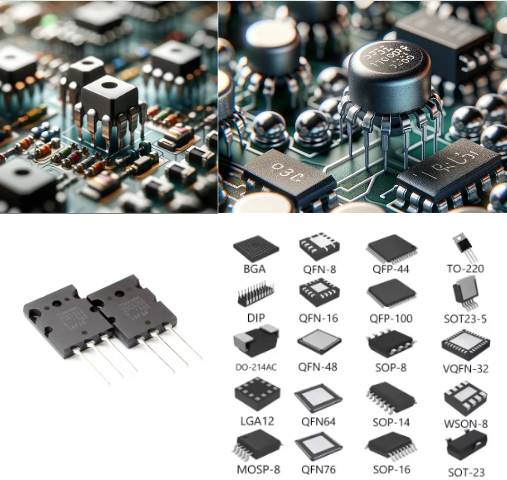
- Appearance: Those consist of all-metal cans or plastic cases.
- Function: Boost or model electrical energy or provide all kinds of power.
6. Integrated Circuits (ICs)
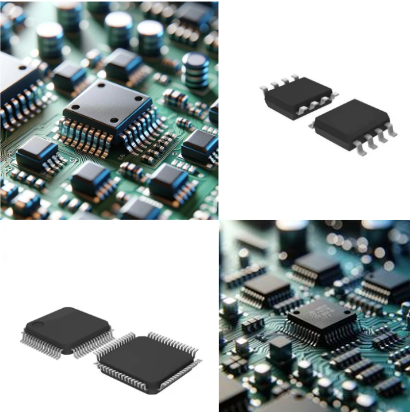
- Appearance: small, cross-like black chips with multiple pins, some of which are labeled with numbers or letters.
- Function: Conduct the simple task of amplification for microprocessor functions.
7. LEDs (light-emitting diodes)
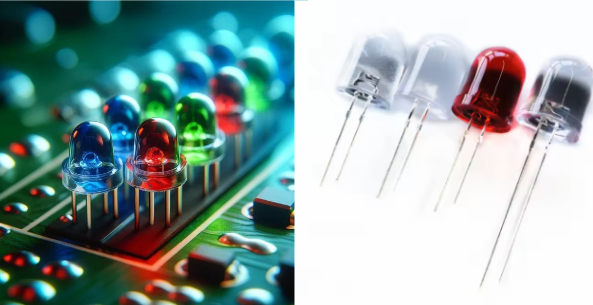
- Appearance: small lenses, or sometimes bulbs, some of them colored to point the light they emit in a certain direction.
- Function: Emit light when subjected to electricity.
8. Switches and Relays
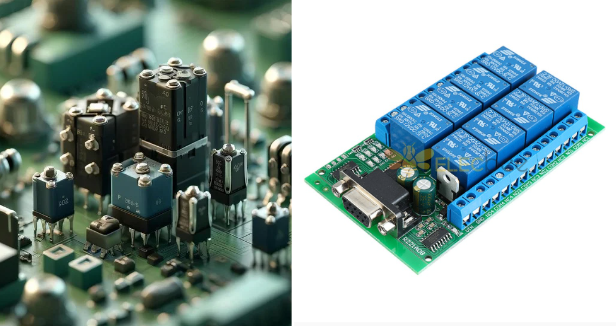
- Appearance: Switches exist alike in size, from little slide switches to considerable toggle switches. Relays are kinds of boxes that contain multiple connections.
- Function: Enable or disable electrical connections manually or select executively depending on electrical system arrangements.
9. Connectors

- Appearance: A lot of variants include specified pin headers and advanced multi-pin layouts.
- Function: Make arrangements to plug or unplug cables from the PCB without soldering.
10. Fuses
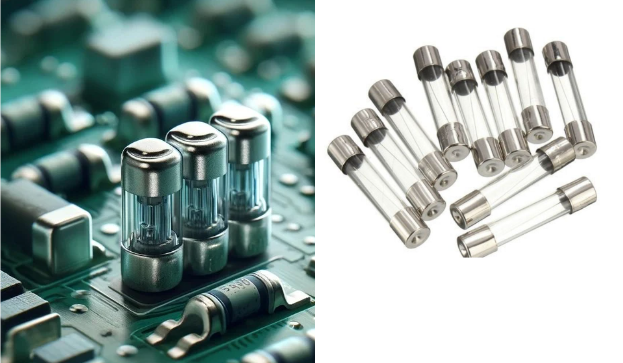
- Appearance: These are small flat (or rectangular) glass or plastic boxes in which the tiny metal strip is visible from inside.
- Function: Safeguard the circuits by disconnecting the link when the current flow goes beyond normal and the line protection switch energizes.
11. Crystals and Oscillators
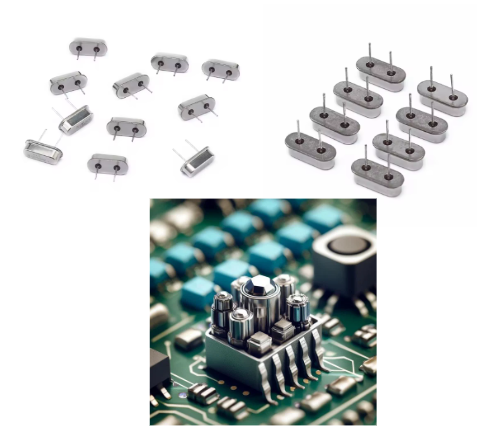
- Appearance: cans of metal or small rectangular packets.
- Function: Supply prescribed frequencies for efficient control of the timings of the circuits.
Identifying Polarized Circuit Board Components

Figuring out contaminated spots on the printed entire circuit board means planning correctly how to assemble the board and function the assembly correctly. Here are some common polarized active components and how to identify them:
- Electrolytic Capacitors: Unlike non-electrolytic capacitors, this type has polarity, which can be symbolized by the black stripe laying along the negative (-) side of the capacitor. The main wire, which is the fattest, is the positive wire, while the thinner one is the negative. At times, the negative lead is chronically designated with a minus (-) sign.
- Diodes: Normally, diodes are known to come with a black or silver band on one end, which differentiates between the cathode and the anode. The second terminal, which is one of the electrodes, is the anode (positive). Also, some diodes can have a line that is usually at the opposite end of the cathode.
- LEDs (light-emitting diodes): the anode of an LED light has a longer positive lead from which it is powered, while the cathode has a shorter negative lead. On the other hand, the cathode side may come with a flat edge or a shorter lead that will be used to connect to other components.
- Polarized Capacitors: Along with the potential danger of certain types of ceramic capacitors being polarized and tantalum capacitors demanding charged polarity, other forms of capacitance—electrolytic—cannot be polarized. They always provide material reinforcement to prevent tears and damage.
- ICs (Integrated Circuits): Chips should possess marks such as notches or dots on pin 1, which is most likely near the end with the plus power (Vcc) pin.
Importance of Circuit Board Components
Component parts of electronics are important for the functioning of devices. Here are some key reasons why these components are important:
- Functionality: Every part of the circuit has its own assignment related to the amplification or control of current flow or the energy storage process. These ancillary elements make it possible for electronic equipment to execute its main tasks as expected.
- Reliability: The top-grade components make electronic devices work more effectively, responsibly, and long-lastingly. Properly design and manufacture components that can be used longer and experience fewer or no failures.
- Efficiency: Components make up the circuit board and therefore enable the efficiency of the electronic instruments. For instance, capacitors can flatten the peaks of voltage fluctuations, while transistors may have clean amplification but low distortion.
- Size and Weight: The size of the components has kept decreasing, and they have become lighter than before; therefore, manufacturers are able to design portable and light electronics.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The multifaceted manufacturing of parts for these devices has dropped prices, thus making electronic devices more affordable for consumers.
- Customization: The combination of the multi-layer components can be used to construct types of custom-made circuits specialized for particular applications.
- Innovation: The new electronic devices and the improvement of the existing ones, which is technological progress, are now possible thanks to developments in component technology.
Briefly, PCBs’s components are key constituents that make the system work; their reliability and efficiency in different sectors and fields are possible.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Printed Circuit Boards Components
The circuit board components are the backbone of the production of an electronic appliance, and these components decide the fate of the appliance. Here are some advantages and disadvantages associated with these components:
Advantages:
- Functionality: Parts of electronic circuits include our friends, variable resistor, capacitors, and transistors, each of which play very important roles.
- Reliability: Bad and failed components are not safe and last for a short time, but they create a hardship for the consumer.
- Efficiency: The components are utilized to provide the right efficiency to the electronic circuits and do not leak the current anywhere, resulting in superior performance and energy conservation.
- Miniaturization: It is worth mentioning that components turned smaller and more close-fitting with time, which resulted in the creation of smaller and more mobile computerized devices.
- Customization: Combining a variety of the components will provide you with the possibility of using ready-made circuits and tailoring them to specific tasks.
- Cost-effectiveness: The cost reduction and mass production of the components have led to cheaper devices, resulting in aggressive competition among companies seeking new market segments.
- Innovation: The newer technologies of component development have brought about the maturation of a new generation of structures and improved the existing ones.
Disadvantages:
- Complexity: With the evolution of electronic devices and their components that are so fine and complex, the number of parts and their interdependency is growing, hence becoming problematic for the manufacturing process.
- Sensitivity to Environmental Factors: Many elements are susceptible to the environmental aspects of temperature, humidity, and electromagnetic interference; therefore, they may only function effectively in the appropriate environment.
- Risk of Counterfeits: In more severe scenarios, materials composited with counterfeit constituents were capable of being introduced into the supply chain, causing reliability and safety problems.
- Obsolescence: The compatibility of devices can be a pitfall, as older components may become obsolete because of emerging technologies to create new and advanced products whose spare parts are hard to find.
- Cost: The high-priced materials can be another issue for the complexes as well as for their specific uses.
- Lead Times: Some of the parts may have long lead times, which finally leads to cutting the production of electronics.
- Compatibility: Making units from individual manufacturers or units involving other specifications than the ones already made can sometimes be a complex activity, and it can slow down the process of production.
Common PCB Components Codes

In PCB (Printed Circuit Board) design, each element is typically assigned a unique point of identification called the “designator” to locate it on the trace and in a sheet.[This sentence could be shorter]. This kind of part-labelling enables the technicians to trace and locate certain components during the installation and fault-detection process. Here’s an explanation of common PCB component codes, including the designator, component type, and their functions:
- R (resistor): The resistor is put on the electric circuit to break the flow of the current and create a voltage drop; the electric power energy goes along with that and dissipates as heat. The current passes through the whole line and then sends it to other components through its method of control.
- Capacitor: Capacitors hold electric energy for a brief period of time and release it when demanded. They can be involved in different usages such as filtering, buffering, and digital signal processing.
- L (inductor): Inductors induct magnetic fields, which store energy when currents flow through them. They are popularly applied in both and have gained authority in filtration and energy storage areas.
- Q (transistor): Transmission and amplifying the signals are performed by transistors. They have the power to handle the outputs, and hence, they are the basic components in digital and analog circuits.
- D (diode): The diodes allow current to flow in one direction only; therefore, they are used for blocking the reverse voltage (opposite of the desired current) and are also utilized for rectifying the power supply units.
- U (Integrated Circuit): ICs that are referred to as integrated circuits are miniature-size chips that perform services modeled on their design, including data processing, the amplification of signals, and power management.
- J (connector): Connectors can be used to connect several parts of the circuit or to make one connect it with the other devices. They are a driving force in aggregating the elements and ensuring ease of maintenance.
- Y (Crystal Oscillator): A crystal oscillator works by using a quartz crystal to generate a fixed, accurate frequency level that is responsible for the clock timing of operations in electronics devices.
- S (switch): In this context, buttons act as endpoints to allow or disallow the current movement of a specific circuit that controls the device’s operation.
- LED (Light Emitting Diode): Forward rotation is a condition where light is emitted from the LED when power runs through it; therefore, current is flowing. Such bow amulets can be both decorative and functional; they normally use something like a pointer for exhibitory purposes.
- F (fuse): Fuses are a type of safety device that melts or disagrees when a current that is greater than the set current level flows through them, hence protecting the equipment against being damaged by excessive current.
- Transformers convert the direct current into an alternating one on the primary side, leveling the amount of voltage on both circuits.
- VR (Voltage Regulator): Voltage regulators are something that is able to output a constant voltage even if the voltage of an input is changed or there is a change in load conditions. This is important for a stable power supply.
How Do You Place PCB Components?
Putting components on the PCB is an important factor in guaranteeing the proper operation and lifespan of the circuit. Here’s a general guide on how to place components on a PCB:
- Component Selection: Select the correct components for your circuit design from the list of available ones that are in line with the specifications and your requirements.
- Component Placement: Pick the schematic diagram and place the components on the PCB based on what is in the schematic. Group nearby parts together in order to reduce signal paths and decrease interference between them.
- Orientation: In cases where polarized components are used, such as diodes, electrolytic capacitors, and ICs, orient them correctly. Depending on the component’s datasheet or schematic, the pin direction can be identified.
- Spacing: Make sure that there is enough distance between the components so as not to form an electric short circuit and for soldering to be easier. Ensure that the components are spaced according to the manufacturer’s build instructions.
- Alignment: Ensure that everything, including lines, axes, etc., is aligned and parallel to the edges of the board for a neat and systematic look. This way of packaging helps with installation and maintenance.
- Signal Integrity: Place key circuits close to what are called oscillators and sensitive analog parts to beat the noises and the power consumption paths.
- Thermal Considerations: Adequate heat removal can be achieved by using different placement methods, directions, heat flows, or heat sinks. Provide enough space for heat sinks or thermal vias to avoid any design discontinuities.
- Mechanical Stability: The integrity of the parts that are mounted on the PCB should be safe from any mechanical stress, such as vibrations or temperature changes, by ensuring that the components are firmly fixed to the PCB.
- Test Points: To cut down on the time spent on the diagnosis and finding the problem, having test points for reaching any segment of the circuit is beneficial.
- Check for Errors: Verify the component placements with respect to the schematic diagram by double-checking the correct devices.
The Circuit Board Components List
An instance of a of a board circuit can exhibit a series of elements, each of which performs some unique function inside the electronic signals device. Here’s a list of common components you might find on a printed circuit board (PCB):
Mechanical Components
Machine parts, that is, gears, levers, and different connectors for the transmission of forces and structural stability, form the basis of machines and mechanisms. Regular machines have several mechanical components. For example, a gear is a common component used to transfer torque between machine parts and also alter speeds by linking their teeth. Another one is a bearing, which can support rotating shafts and reduce friction. The structure can store mechanical energy while it is compressed or stretched into the surface mount technology. Intense parts are such things as screws, which screw materials together and can transform rotational motion into linear motion; belts and chains that perform sideways directive functions between pulleys or gears; and levers, which maximize input force to produce a larger output force. Each of these three pillars plays a decisive role in the mechanical performance and overall effectiveness of many tools and machines, which therefore forms the basis for modern engineering and design.
Electrical Components
Electrical elements, although seemingly small components, serve as crucial factors for the working of electronic circuits, where each component has a particular function of controlling, directing, and manipulating the flow of electricity in devices and systems. Some of the main components are resistors, which control current levels and manage voltage matters in tuning and filtering applications; capacitors, which crucially store and release energy for various purposes; and besides that, inductors store the energy, thus creating magnetic fields that are sometimes used in filters and transformers. Bipolar Transistor, as well as the base for the signal boost and switching technique, and diodes, enabling current in one direction to pass, are the prime components of a full electronic device. Integrated circuits (ICs) merge all these components into one. As a result, it became a miniature and efficient product that performed complex tasks. Moreover, switches, relays, and connectors are the main components that actually become the building materials used in controlling circuit connections and flow paths. These components function as a group to bridge the divide between simple gadgets and the complex computing machinery that is often the foundation of sophisticated and functional electronic systems.
Passive Components
The invaluable passive elements complete the circuit diagram of the various electronic circuit without requiring any sort of power (other than the electrical circuit current which is flowing past it). One of the common components is resistors, it is also a capacitor and an inductor. Besides load or consumption of energy when very high current flows, resistors also offer control of current and voltage levels within the circuits providing specific resistance value which is used to manage current flow. Like a reservoir, capacitors are able to store and release electricity. Therefore, they are often used in filtering circuits, tidal waves that are sent to batteries, and more electric energy reserve systems. Inductors, just like capacitors, contain energy in the form of magnetic fields, when there flows through the current. Inductors are quite common in power supplies or radio frequency circuits. These constitutive components of monitors and electrical devices control and stabilize different means of transmitting electrical signals and energy, which is very necessary for the proper working of virtually every electronic device.
FAQS
For those interested in the components and functionalities of a circuit board, here are some important FAQs that can provide clarity and essential knowledge:
Conclusion
Proper PCB design and efficient arrangement of components enhance the device performance, consequently prolonging its woking lifespan and reducing repair costs. Due to the referred to knowledge of the roles of each component of the circuit board, engineers can perform their task better and hobbyists can enjoy themselves by more competently designing and realizing their own circuits. In your journey of developing more knowledge on electronics or starting with some project of your own, having an understanding of circuit board components concepts is the initial step towards your goals.

