With more advancements in technology, managing electronic devices has become an extremely important issue. Often, device maintenance has a very critical factor, which is to clean electronic circuit boards. Besides running safe and dependable computational tasks, clean circuit boards are critical in avoiding tolerance interferences caused by accumulations of dust, dirt, and other impurities.

In this article, we are going to cover up the process in cleaning the circuit boards, the tools and materials needed for it and then the step-by-step process of cleaning them and at the end, some advices that will help your devices run depending on how you clean them.
Importance of Cleaning Circuit Boards
The main building blocks of all electronic appliances are the printed circuit boards, which, being the most important part, contains various connecting elements of electronic circuits. Long-term, environmental factors work their way in contaminating the machines which vacuum oil, dust and corrosion.
In addition to improving the electronic printed circuit board for protection against electrical shorting and failures, cleaning delicate circuit boards also has the advantage of lengthening the life expectancy of the device.
Precautions Before PCB Cleaning
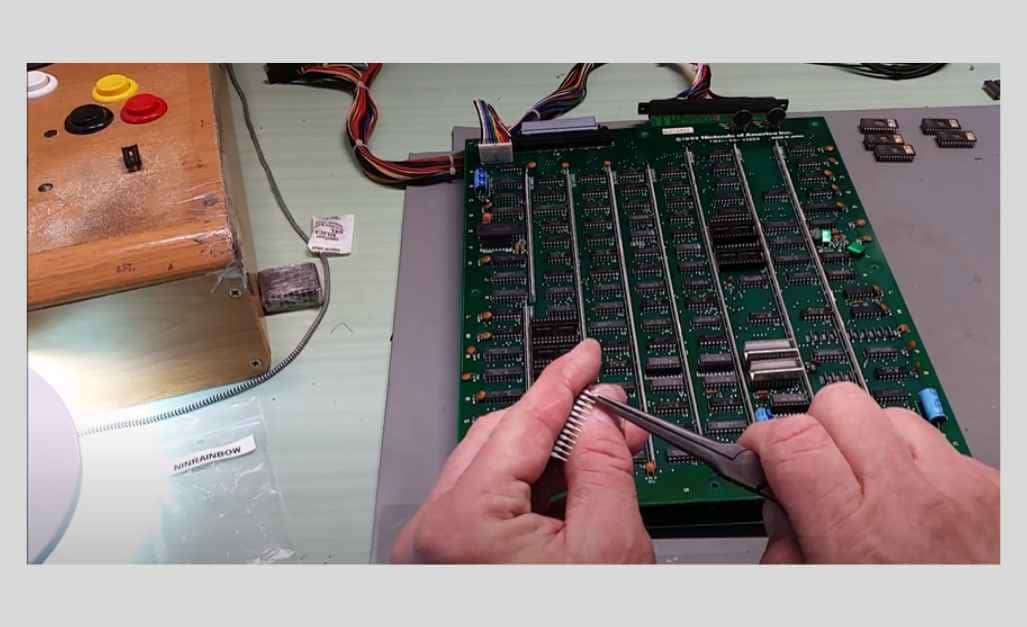

Power Down and Unplug: The implementation of safe procedures is just as crucial as the cleaning activities. Remember to ensure that the device is fully turned off and completely disconnected from its power source before you start cleaning the circuit board.
Discharge Capacitors: Whenever you are dealing with capacitors, check for charging and release them before working. This ensures that proper protection from electric shock risks is observed at all times.
Handle with Care: The circuit board is a very delicate brush small equipment with an engineering work of art. Use both your hands to handle them carefully and save them from being touched on the delicate parts and solder points with the chance of accidental damage to the unit.
How do Circuit Boards Get Dirty?
The circuit boards electronic devices are integral to diverse devices; they may be contaminated, implying consequences to their effectiveness and functionality, respectively. Correct grasping of the might result of contaminations and the risk they can cause is very important in reliability in the field of circuit boards. We will elucidate all the subfactors of dry contaminants, wet contaminants, corrosion and solder flux residues in the coming paragraphs.
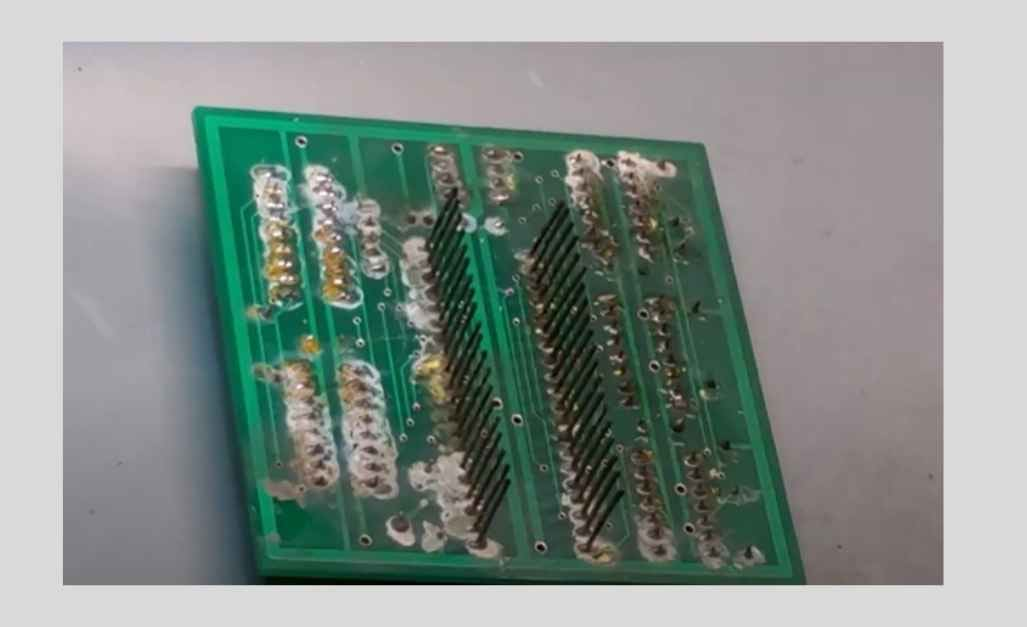
A. Dry Contaminants

Dry contaminants like dust, fibers, and metal shavings deposit on top of circuit boards when exposed to the environment or as the result of poor manufacturing processes or the improper handling and storage of components. Such contaminants can induce circuit failures, lead to reduced heat dissipation, and affect electric connections, thus causing a breakdown.
B. Wet Contaminants
Such liquids cause damage to circuit boards as a result of moisture and oils. This can occur through humidity, condensation, spills, leaks, or the use of improper cleaning solutions. These pollutants can be reasons for short-circuiting, corrosion, and long-term deterioration of fatigue to the board’s components and connections, causing the high risk.
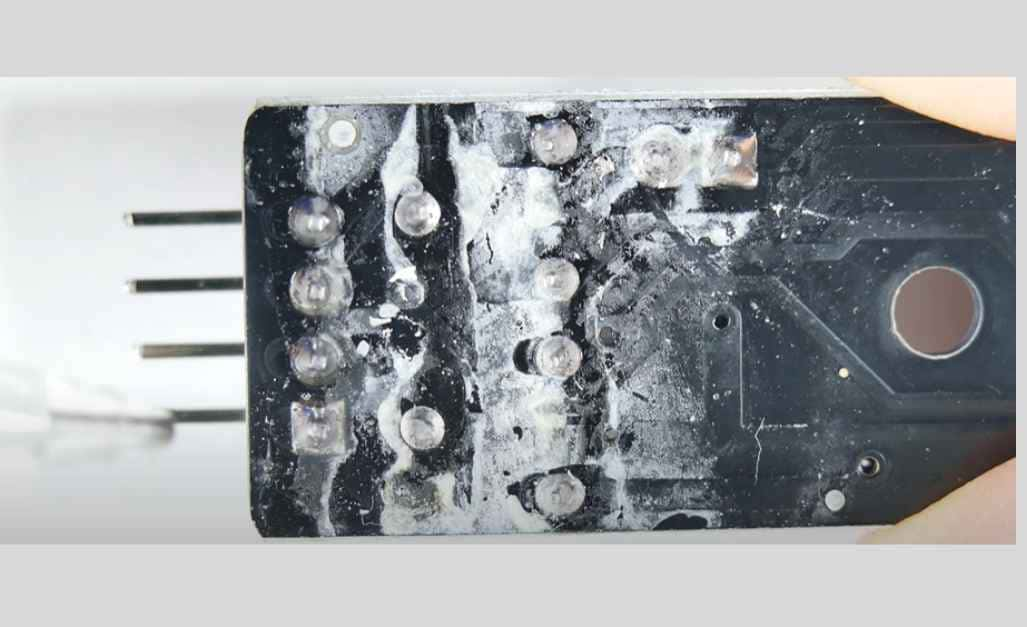
C. Corrosion

Corrosion is the process that leads to a metal reacting with environmental elements and, consequently, the deterioration of metal surfaces. The main causes are related to humidity, contagions, pollution, and dust. Corrosion may lead to the electrical connections also being compromised, which in turn may cause both increased resistance and circuit faults.
D. Solder Flux on Circuit Boards
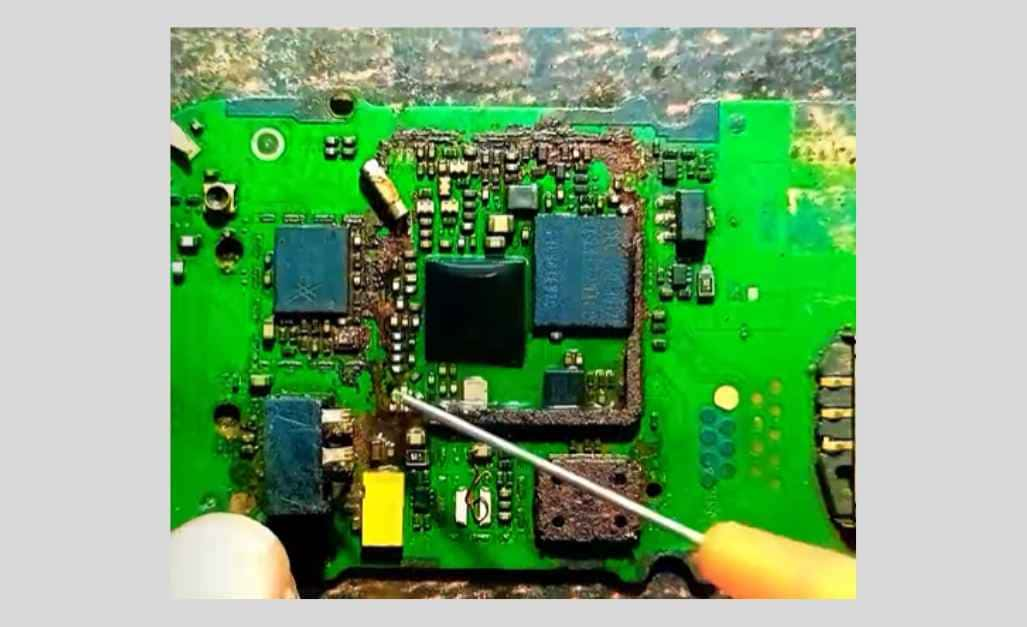

Solder flux, used in the soldering process, can cause issues like electrical interference, corrosion, and aesthetic concerns on circuit boards. If not cleaned properly, residues can create conductive paths, promote corrosion, and attract contaminants, affecting the board’s aesthetics and reliability.
Materials Needed for Cleaning Electronic Circuit Boards
These are the materials needed for cleaning electronics circuit board:
1. Isopropyl Alcohol (IPA)

This is probably one of the most popular PCB cleaning agents for bar cleaning after rubbing alcohol. It is one of the great things about it that it underlies dissolving the flux residues, oils, and other filth without damaging the board.
2. Flux Remover
This is a unique task that involves the use of flux removers as specialized cleaning solutions to clean flux residues from PCB.
3. Ultrasonic Cleaner

This is considered the most efficient cleaning method of PCBs because it is very effective for difficult residues and contaminants in the hidden corners of the boards.
4. Brushes
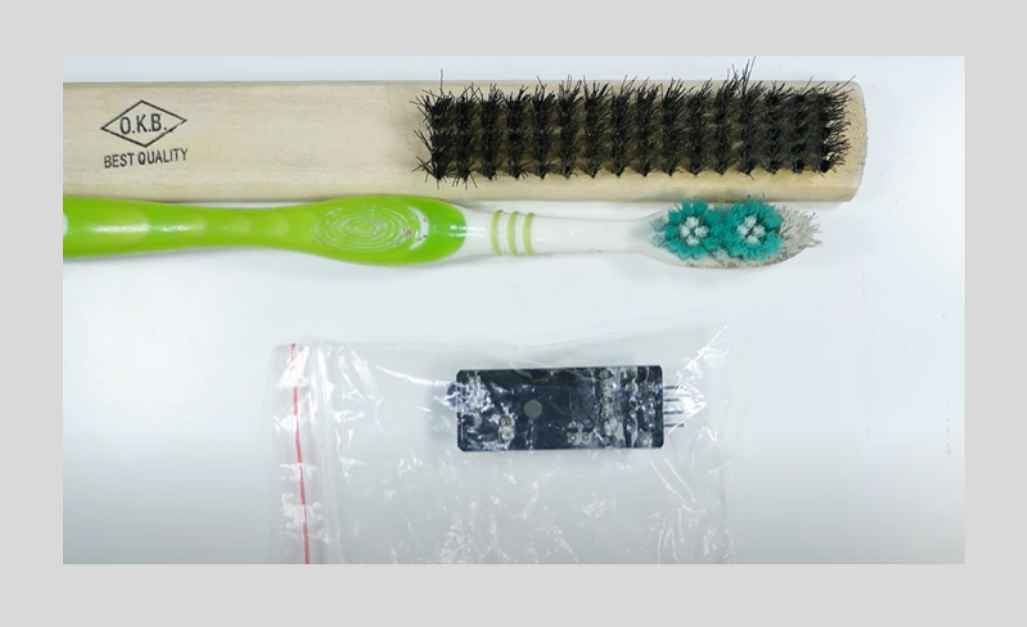

Brushes of different types, especially soft-bristled brushes, are the necessary accessories for manual cleaning of PCBs, apart from the use of chemicals and machines. Gently textured bristle brushes are meant for light cleaning, while those with hard bristles can get rid of more tough deposits.
5. Compressed Air
Pressurized Air gets into the picture to also remove dirt, dust and dead material by sweeping them away from the PCB. Its portability makes it ideal for the quick clean-up of small spots and also for those hard-to-reach areas where it would normally be difficult to use a brush.
6. Lint-Free Towels
Lint-free towels are incredibly crucial, as they help us clean PCBs without generating unwanted fibers or particles.
7. Cleaning Tick of the Soldering Iron
This is a kind of cleaner that is designed to clean soldering iron tips but can also help in total cleaning of solder joints on PCB boards.
8. Deionized water
This is used for rinsing PCB after cleaning them with select rapid water-responsive solvents or ultrasonic cleaning. Such a process guarantees that a person will have no stains on the board.
Printed Circuit Board Cleaning: A Step-by-Step Guide
These are the step by step guide:
Cleaning Dry Contaminants on Circuit Board
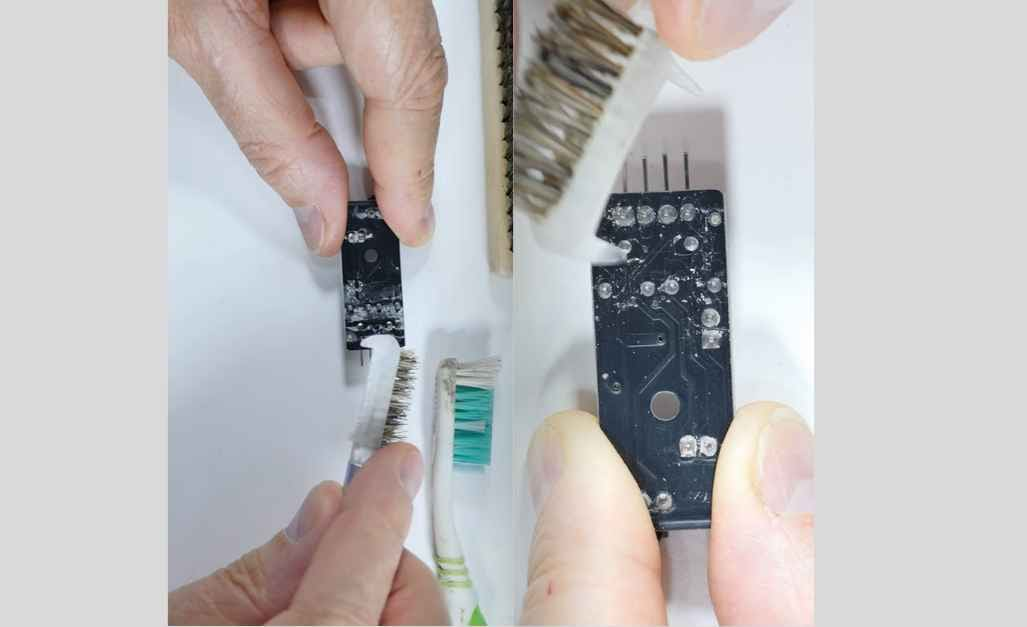

1st Step: Prepare Your Workspace
The workspace setup is done by first powering down and unplugging the circuit board. This should go to a clean, well-lit area where you have an anti-static mat and safety gear you can wear.
2nd Step: Initial Dust Removal
The venture to clean dust from free circuit boards will employ properly directed pressure air and a tiny-nozzle vacuum cleaner to avoid static discharge.
3rd Step: Manual Cleaning
To manually clean an anti-static soft bristle brush and tweezers to eliminate dust, dirt, and whatever else from the board in such a way that contaminants will not be redistributed.
4th Step: Final Touches
Use microfiber cloth to wipe circuit board, eliminating dust compounds. However, do not forget about close inspection of the process.
Final Step: Preventive Measures
Employ an anti-static wrist strap during cleaning to prevent ESD damage and schedule routine maintenance in order to eliminate dust accumulation in roller furnaces.
Cleaning Wet Contaminants on Circuit board
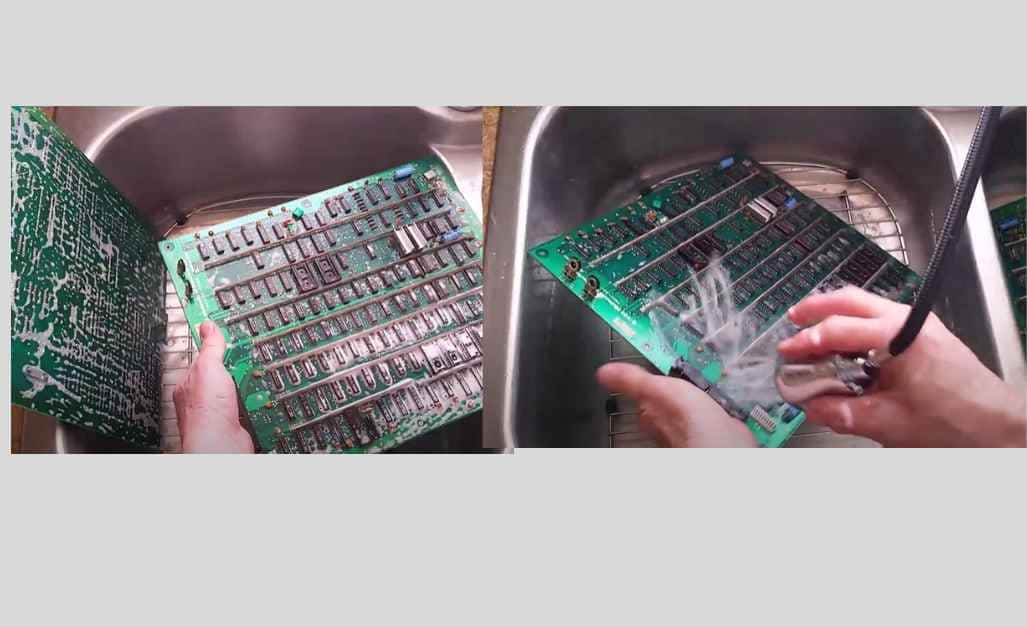

Step 1: Preparation
In preparation, deactivate the circuit board, unplug the batteries and all the external elements, and wear an antistatic wrist strap to prevent any static damage to sensitive components.
Step 2: Rinse
The circuit board must be gently washed with distilled water and light components will not dislocate on the rinsing.
Step 3: Clean up with Isopropyl Alcohol
Isopropyl alcohol is used to clean circuit boards by submerging them in the alcohol, gently using a soft brush to scrub the area, and allowing the entire board to soak before cleaning with a brush all over again.
Step 4: Rinse and Dry
Run the circuit board through fresh isopropyl alcohol after scrubbing with a brush to expel the impurities. Finally, use compressed air canister for drying.
Step 5: Drying
The board should be cleaned with an extremely fine-threaded cloth to avoid ruining it. Air-dry on paper towels. It is vital to let the board dry completely before reassembling or powering it up.
Step 6: Inspection and Assembly
It involves checking for residual dirt on the circuit board, replacing the parts, reassembling, and re-checking part after part after cleaning and drying.
Clean Corrosion on Circuit board
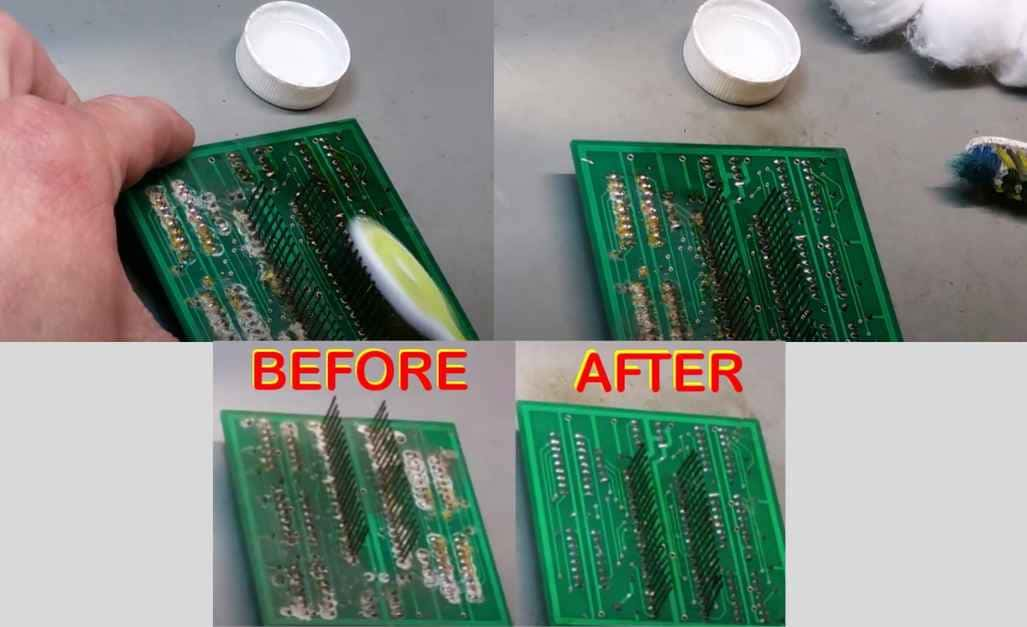

Step 1: Safety Precautions
Close the circuit board of the vehicle and work in the well-ventilation area with the use of safety gloves, hand protection, and eye protection to prevent contact with cleaning agents.
Step 2: Initial Cleaning
The board is to be inspected for corrosion and any regions that are affected by the brushing of dust and debris with the use of a brush or compressed air.
Step 3: Prepare a cleaning solution.
When washing, use a circuit board cleaner spray declared to contain 90% IPA. A severe corrosion case is cleaned using a baking soda paste with distilled water.
Step 4: Cleaning Process
On the other hand, for corrosion cleaning, one can use the IPA with a cotton swab or toothbrush and baking soda paste to remove the toughest corrosion. It requires good brushing with a soft brush, rinsing with distilled water, and then drying the clothes thoroughly. To get rid of the residue, wash with IPA.
Step 5: Drying
Air drying is used to remove any moisture from the drying circle while open air is used to leave the board open during drying. Detaining the board for its assembly or turning it on before total drying is not advised.
How to Remove Solder Flux Residues
Step 1: Prepare yourself by working in an area that is well ventilated, and also wear gloves and safety glasses in order to prevent inhaling the fumes that come with cleaning solvents.
Step 2: First cleaning stage consists of swiping Isopropyl Alcohol or Flux Remover, followed by methodical cleaning with a static-free brush in small area to restrict spreading flux residue.
Step 3: Repetitive cleaning of the PCB by re-applying the cleaning solution with the help of the ultrasonic cleaner on the basis of the manufacturer’s instructions concerning the duration of heating and the solvent compatibility.
Step 4: Cleaning the board with IPA again after the scrubbing will help in removing any flux and solution that may have been loosened during cleaning and make sure there is no residue left.
Step 5: Blow compressed air to the PCBs to dry them quickly to avoid hazardous moisture accumulation. Continue till it dries up up completely without being blown or exposed in any dusty atmosphere.
Step 6: Then you would have to perform a visual inspection to remove flux dregs and after this perform a functional test to verify that the connections are in good functional condition, and consider problems.
Tips in Maintaining and Cleaning circuit boards
Regular Inspections: Dust your boards every day or if you are working with circuit boards with polymers or plastic for days. You need to check whether there is dust, debris or rust. Proactive plans before these effects occur can mitigate the risks.
Avoid Liquid Cleaners: It should be noted that in case of circuit boards it is better to avoid using liquid cleaners as they can be harmful to the circuit board. It can harm the sensitive components of the device and lead to short circuiting.
Anti-Static Measures: While working with the circuit boards, utilize anti- static tools and also work in an Electro static discharge (ESD) protected workspace.
Proper Storage: When storing unused circuit boards, it is important to avoid dust and moisture accumulation and damage from physical contact. The most common storage method for circuit boards is to put them in anti-static bags or container.
Regular Maintenance: Consequently, you should educate your customers and other users about the benefits of circuit board cleaning and maintenance in proper device management. This type of preventive maintenance can help to avoid destruction of your devices.
Avoid overloading: Similarly, stuffing many functions into a circuit board may result in high temperatures and poor energy consumption. When designing the circuit, make sure to follow the manufacturer’s placement of the components and calculations of the components’ power.
Professional Cleaning: If the circuit board is very dirty or consists of complex layers, it is wise to entrust the cleaning work to professionals. They need to use special tools and techniques to clean electronics without damaging them.
Challenges in Cleaning Circuit Boards
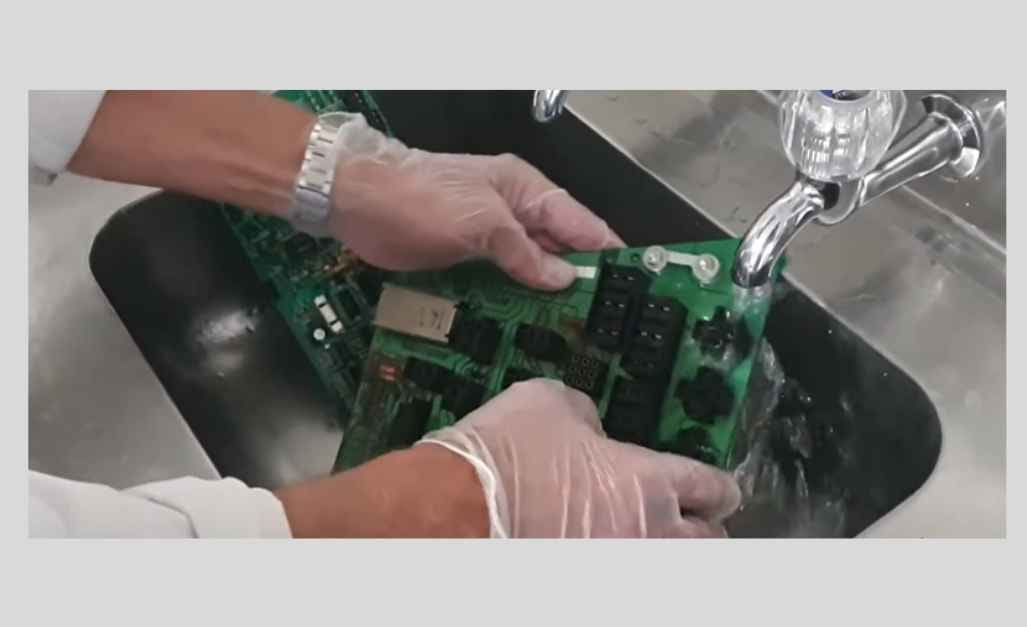

Cleaning circuit boards is a critical process in ensuring the reliability and longevity of electronic devices. However, it comes with several challenges that need to be addressed to maintain the integrity of the components and the overall functionality of the board.
1. Delicate Components
One of the difficulties with the cleaning of today’s circuit boards is that they can be highly sensitive to damage, notably caused by small and fragile parts. The cleaning practices must be mild and careful enough to attempt neither dislodge nor harm these components.
2. Complex Geometries
Integrated circuits included in electronics can have a very complex shape with many key spaces, detailed routes and lots of compact components. The fact that the entire region that is to be decontaminated can be highly difficult means that special technologies and methods must be utilized.
3. Residues and Contaminants
Different kinds of of dirt and residues, like flux, solder paste, dust and oils, can be found on circuit boards. Many forms of contaminants require specific cleaning methods or different solvents, thus increasing the difficulty of the whole cleaning process.
- Compatibility with Cleaning Agents
A careful consideration should be made of the agent to be used because some of the solvent can be too harsh and may damage the board and its components. Multiple variables of compatibility need to be taken into account not only for circuit board materials but for components as well to prevent chemical damage.
5. Static Discharge
Static electricity creation can be seen during the cleaning process, and this has a high risk of overheating and component failure in electronic devices. Proper grounding and static-control measures are critical to eliminating the danger of damage due to electrostatic discharge (ESD).
FAQs
Conclusion
Cleaning circuit boards is a crucial aspect of electronics maintenance and manufacturing. It ensures the reliability, longevity, and optimal performance of electronic devices. In conclusion, proper cleaning techniques, such as using the right cleaning agents, methods, and equipment, are essential to cleaning wet contaminants, residues, and debris from circuit boards.

