Rigid PCBs
Flexible Order Quantities
We offer Rigid PCB production with no minimum order quantity, ensuring flexibility and cost-effectiveness for all project sizes.
Rapid Prototyping and Production
- Sample: 3-5 Days
- Mass production:8-10 Days
Advanced Layering and High Density
- Layers:4-32
- Versatile Layer Interconnectivity
Expert Technical Support
- One-on-one engineering services
- 24/7 Customer Service Online
- Flexible design
Rigid PCB Definition
What is a Rigid PCB Circuit Board?
Rigid PCBs are a type of Printed Circuit Board and are the most commonly manufactured. They are built using solid substrate materials, which help prevent the board from warping. One of the most familiar examples of a rigid PCB is the computer motherboard, a multi-layered PCB that distributes power from the power supply and facilitates communication between essential components like the CPU, GPU, and RAM.
Rigid PCBs are ideal for situations where the board must maintain its shape throughout the lifespan of the equipment. These can range from simple single-layer designs to complex multi-layer configurations with up to eight or ten layers.
Rigid and flexible PCBs differ significantly, with rigid PCBs being solid and inflexible, while flexible PCBs can bend. As a result, their applications vary. There are also Rigid-Flex PCBs, which combine elements of both. All rigid PCBs, whether single, double, or multi-layer, share common areas of application due to their structural characteristics.

RIGID PCB
All rigid PCBs come in single-layer, double-layer, or multi-layer constructions, and they share similar applications due to these structural configurations.
Rigid PCB Examples
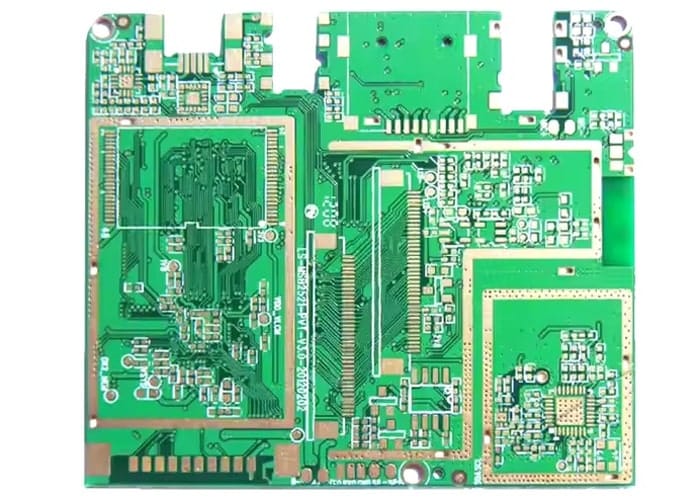
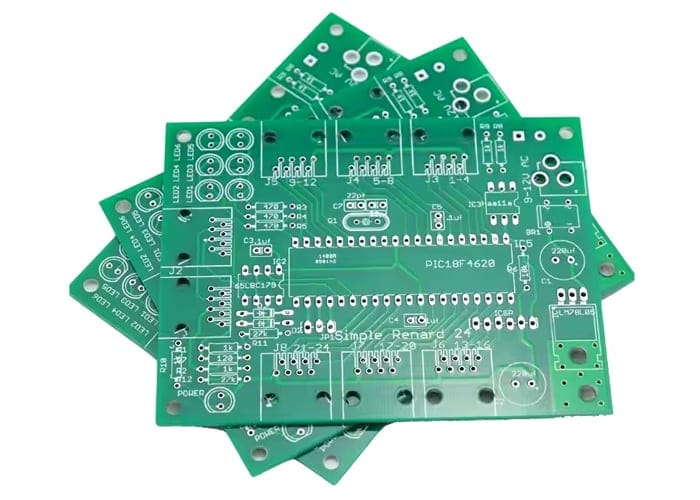

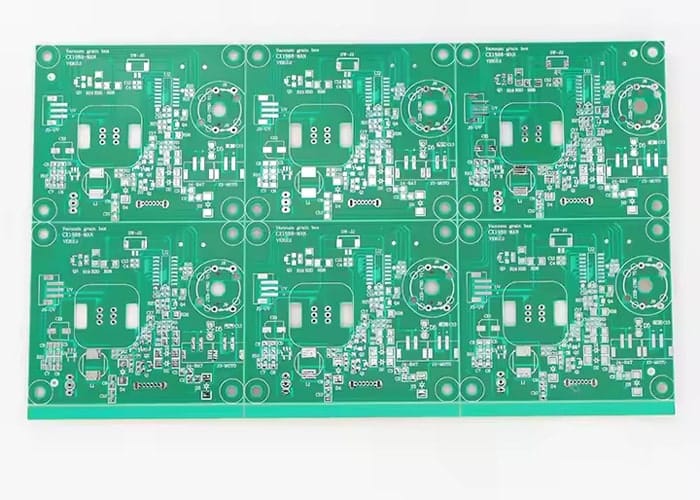

Characteristics of Rigid PCB
01
Rigid PCB is a type of traditional PCB that differs from Flexi PCB, as it cannot be bent or folded into various shapes. This is due to its FR4 reinforcement, which effectively enhances its rigidity.
03
The computer motherboard is a prime example of a rigid PCB featuring a solid substrate material.
05
Rigid PCBs are more affordable than flexible PCBs. As traditional PCBs, they are commonly used in a wide range of electronic devices.
02
Rigid PCBs consist of copper traces and pathways integrated into a single board to connect various components. The board’s base material is a rigid substrate, providing it with both strength and stability.
04
After rigid PCBs are produced, they cannot be altered or bent into different shapes.
06
Flexible PCBs and rigid PCBs each have their own advantages and limitations regarding ease of use and availability. Both types are employed to connect multiple electronic components on circuit boards.
How Are Rigid PCB Boards Manufactured?
What are PCBs made of?
A rigid PCB is made up of multiple layers bonded together with adhesive and heat, giving the board material its solid form. The following layers are used in the construction of a rigid PCB.
Rigid PCB stack up and materials for manufacturing
Substrate Layer
The substrate layer, also known as the base material, is made from fiberglass.
FR4 is the most commonly used substrate material, providing the board with its rigidity and stiffness due to its fiberglass composition.
Phenolics and epoxies are also used as base materials, but they are inferior to FR4. However, they are more affordable and have a distinct unpleasant odor.
Phenolics have a low decomposition temperature, which can lead to layer delamination if solder is applied for an extended period.
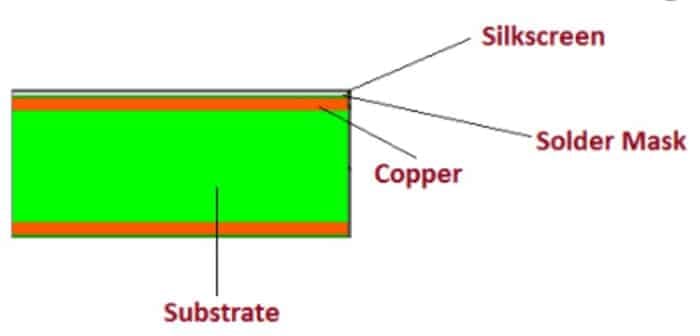

Copper Layer
A copper foil is laminated onto the substrate layer using heat and adhesive.
Typically, both sides of the board are laminated with copper, although some low-cost electronics only have one layer of copper.
Boards come in various thicknesses, measured in ounces per square foot.
Solder Mask Layer
The solder mask layer sits above the copper layer.
This layer is applied to insulate the copper and prevent damage in case any conductive material comes into contact with it.
Silkscreen Layer
The silkscreen layer is positioned above the solder mask layer.
It is used to print characters or symbols on the board for easier identification and understanding.
While white is the most common color for silkscreen, other options like gray, red, black, and yellow are also available.
The Differences Between Rigid PCBs and Flexible PCBs
Most electronic devices traditionally used rigid PCBs. However, as technology advanced, many products moved away from rigid PCBs due to their inability to bend or twist. This led to the development of flexible PCBs, which quickly became a preferred choice for many professionals in the market.
The manufacturing processes of rigid and flexible PCBs are mostly the same, with differences in their flexibility, softness, and cost.
Handling flexible PCBs requires additional precautions, especially to prevent cracked solder joints when the board is bent. Specific design considerations must be followed for material handling during production.
Flexible PCBs are generally more expensive than rigid PCBs. While the individual cost of a flexible PCB is higher, the overall project cost using rigid PCBs could sometimes surpass that of flexible PCBs. Still, on a unit basis, flexible PCBs are pricier.
Rigid PCBs are commonly found in inexpensive electronics, such as audio keyboards, desktop devices, solid-state drives, toys, and various electronic gadgets. In contrast, flexible circuits are used in high-performance devices due to their thinner form factor, making them ideal for smartphones, cameras, tablets, and GPS systems.
Both rigid and flexible boards can be combined to create products that offer both strength and flexibility.
Although some flexible PCBs share a similar design with rigid circuits, they are not identical.
Flexible PCBs offer the advantage of bending and saving space, and they are often used in single-sided PCB designs.

When to Use Rigid PCBs and When to Use Flexible PCBs
- Rigid PCBs are generally less expensive than flexible circuits. However, in some cases, when considering the total cost of ownership, using flexible PCBs may actually be more cost-effective than rigid ones. This is because flexible circuits can eliminate the need for additional components like connectors, wire harnesses, and extra circuit boards. By removing these components, material, labor, assembly, and scrap costs are reduced.
- Many electronic devices, such as laptops, desktop computers, audio keyboards, solid-state drives (SSDs), flat-screen TVs, monitors, children’s toys, and various gadgets, use rigid PCBs. In contrast, flexible circuits are often found in ultra-compact or high-performance devices like GPS units, tablets, smartphones, cameras, and wearables.
- Flex circuits aren’t just for sophisticated applications; even low-tech products like LED lights may use flexible circuit technology in some cases due to its ease of installation.
What are the rigid PCBs used for?
Rigid PCB Applications
computer motherboard
The computer motherboard is an ideal example of a rigid PCB, specifically a multilayer rigid PCB, used to distribute power from the power supply and establish conductive paths between the CPU, GPU, and RAM.
Electronic products
Certain low-cost products, such as toys, electronic gadgets, desktop devices, and solid-state devices, utilize rigid PCBs.
Others
It's also worth considering Double-Sided PCBs, which are another type of rigid PCB.
Different Types of Rigid PCB Provided by Camtechpcb
Single-Sided PCB: These rigid printed circuit boards have metal traces on only one side of the dielectric layer. Single-sided rigid PCBs are ideal for quick production due to their simple design and ease of manufacturability.
Double-Sided PCB: As the name implies, these PCBs feature a dielectric layer sandwiched between two metal layers. Double-sided rigid PCBs are widely used in the industry for various applications, including low to high-temperature conditions, fine-line surface mounting, solder coatings, and high copper builds.
Multilayer PCB: Multilayer rigid PCBs consist of more than two conductive metal layers, separated by dielectric layers. These boards offer designers the flexibility to create complex interconnects and support a wide range of applications.
Camtechpcb is dedicated to delivering top-quality rigid Printed Circuit Boards at competitive prices. These PCBs use a solid, inflexible substrate material such as fiberglass, which ensures rigidity and prevents bending. We offer high-performance rigid printed circuit boards in various specifications to meet diverse needs.
Discover more about Camtechpcb by exploring our manufacturing capabilities for rigid PCBs. We deliver more than you can imagine.
FAQ
Flexible printed circuit boards, also known as Flexible PCBs or Flex PCBs, get their name from their ability to adapt the circuitry to fit the design of the electronic device or product, rather than designing the device to fit the circuit board.
The most common substrate used in printed circuit boards is fiberglass-reinforced epoxy resin, with copper foil bonded to one or both sides. More affordable PCBs, often used in household electrical devices, are made from paper-reinforced phenolic resin with bonded copper foil.
Copper is an outstanding conductor of electricity and heat, enhancing heat transfer across the PCB. This helps reduce harmful stress from uneven heating, which could otherwise lead to micro-fractures in the PCB and potential device failure.
The most common causes of PCB failures are often linked to component design issues. Examples include improper component placement, power failures, and overheating due to insufficient space on the PCB, all of which can occur during the design and manufacturing stages.
We are a factory with our own PCB manufacturing and assembly facilities.
We provide a one-stop service, covering everything from PCB manufacturing and assembly to testing, housing, and additional value-added services.

