To design a printed circuit board (PCB), the PCB copper thickness is among the key issues that need to be accounted for. Copper is the most preferred material and is used as a conduction material for electricity, and the thickness of the copper’s inner layers will largely influence the performance and affordability of the board. There are two types of thickness for copper: 2 oz and 1 oz, Each has two different features, but they are recommended for different applications. In this article, we will examine the question of choosing between 2oz and 1 oz of copper and discuss which thickness is right for your PCB application.
Understanding Copper Thickness
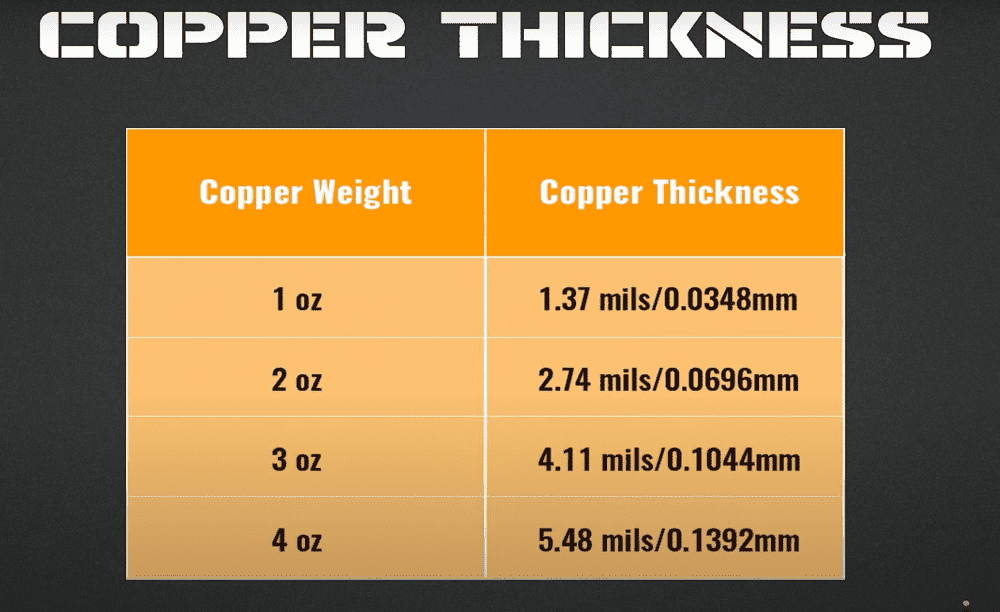
Before focusing on the 2 Oz and 1 Oz PCB copper thicknesses, a basic understanding of these terms is needed. Copper thickness is normally measured in ounces per square foot (oz/ft2) and in micrometers (μm). An ounce of copper is expected to have a finished copper thickness of 1.37 mils, or 35 micrometers in thickness. Thus, 2 oz. of copper is about twice as heavy as 1 oz copper evenly.
Importance of Copper Thickness in PCBs
Conductivity: Copper is the best conductor of electricity. The thicker layers of copper result in a lower electric resistance, which helps in the efficient transmission of electrical signals throughout the printed circuit board.
Current-Carrying Capacity: The current carrying capability of copper traces on a PCB has a direct relationship to their thickness, since copper traces that are thicker will not overheat or experience voltage drops.
Heat Dissipation:Thicker copper layers are needed for heat dissipation, a very important property because electronic components are the source of heat during operation.
Durability: Thicker copper layers increase the mechanical strength and durability of the PCB, which in turn makes it less susceptible to damage caused by mechanical activity during handling, soldering, and environmental conditions.
Copper Features When Choosing Thicker Copper
With regard to which PCB thickness you should choose, consider your present demands related to the intensity of the current, heat generation as well as your cost limitations along with the capability of the manufacturer to produce sheets of the desired thickness.
Thicker copper layers surely prevent those components from overheating and add even some voltage drop while making heat dissipation inside components such as power electronics.
A. Copper Weight
The copper weights in a PCB,commonly called as copper thickness, can be expressed in both American (oz/ft²) as well as Metric units (µm). Common copper thickness options for PCBs include: Common copper thickness options for PCBs include:
1 oz Copper (35 µm):
This is the set copper weight, which is generally given in most PCBs. The material is a perfect conductor and is thus suitable for a broader range of applications.
2 oz. Copper (70 µm):
Double the thickness of 1 oz copper, 2 oz copper offers lower resistance and is used in applications where heavier copper and higher current carrying capacity or better heat dissipation is required.
Other Thicknesses:
In addition, the PCB principle is also valid for copper thickness of 0.5 oz (17.5 µm) and flawlessly satisfying 3 oz (105 µm) in exceptional situations of its final thickness.
B. Copper Foil
In a PCB (Printed Circuit Board) copper foil denotes the thin layer of copper being attached (laminated) onto the PCB’s carrier (substrate). It performs the most critical function and is responsible for the board establishing the conductive traces between various electronic devices that are provided on the board.
Copper foil has proven to be a material with excellent conductivity for carrying the data lines across the Printed Circuit Boards. Its thicknesses are different variations, it bonds different layers of material with the adhesive layer, creates trace conductors with selective etching, and may also be plated for high thickness.
1 Oz Copper Thicknesses
The 1 oz copper thickness of a printed circuit board (PCB) is being measured in ounces per square feet (oz/sqft). On 1 oz copper, in particular, you can find roughly 35.56 micrometers (board thickness as much as 1.4 mils or 0.0014 inches) of copper on only one side of the PCB. Therefore, this value is a staple in PCB production and is applied in plenty of electronics applications that tend to precisely combine acceptable performance and affordability.
A. Advantages of 1 oz Copper Thickness
- Using 1 oz copper is more economical as compared to thicker options such as 2 oz or 3 oz, hence being the preferred choice for cost optimization applications.
- 1 oz copper gains flexibility in PCB design, covering moderate thickness which balances cost, performance, and manufacturability, It is also low density and suits many electronic devices.
- With only 1 oz of copper, this board is still a powerful conductor of the electrical energy, and consequently, the signal transmission and power distribution is very efficient across the PCB.
- One ounce of copper has reasonable thermal conductivity, although it is not as effective as thicker copper layers for heat dissipation in electronic circuits.
B. Applications of 1 oz Copper Thickness
- Consumer Electronics: The 1 oz copper thick PCBs most commonly used in the consumer electronics, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, choose their performance and cost balance.
- Industrial Control Systems: The metals sector favors 1 oz copper for reliability and cost effectiveness, and is commonly used in medium-power industrial equipment and control systems.
- Automotive Electronics: In automotive applications, where space and weight are very crucial, 1 ox copper is usually present in PCBs for various electronic systems in a car.
- IoT Devices: Thanks to the growing number of IoT devices, 1 oz copper is favored for its proficiency in providing divergent circuit designs while the production expenditures of the same remain low.
2 Oz copper thicknesses

A copper-clad PCB that is 2 oz copper thick or 70 µm in thickness (2.8 mills) for a copper layer on a printed circuit board (PCB) is also mentioned. The thickness of copper in the PCB is measured in ounce per square foot (oz/ft²). In this case, the 2 oz stands for the weight of the copper per square foot of that its sample area. With this, the copper layer thickness may affect the board carrying current, the dissipating heat and the ability to endure mechanical stress.
A. Advantages of 2 Oz Copper Thickness
- A 2 oz copper thickness has a higher current carrying capacity hence, it is suitable for the power electronics and the applications that require solid electrical conductivity.
- Thicker copper layers improve thermal control by efficiently dissipating heat, minimizing component overheating hazard, and increasing system reliability.
- PCBs which come in 2 oz copper thickness provides excellent durability and resistance against mechanical stresses, therefore being suitable for harsh environments or applications requiring frequent handling or vibration.
- A thicker profile of 2 oz copper allows flexibility in design, allowing for creation of intricate trace patterns and compact designs, thereby improving performance.
B. Applications of 2 Oz Copper Thickness PCBs
- Power Electronics: 2 oz copper is an advantage for inverters, motor drives, power supplies, and high-current circuits by improving the conductivity and heat dissipation.
- Automotive Electronics: PCBs in automotive systems, for instance engine control units (ECUs) and electronic control modules (ECMs), often use 2 oz copper for robustness under harsh conditions.
- Industrial Control Systems: PLCs, industrial automation equipment and control panels are dependent on 2 oz copper for high performance and long life.
- Aerospace and Defense: PCBs of aerospace and defence applications have very high reliabilities and abilities to work under any circumstances, and thus 2 oz copper is a favourite selection.
Choosing the Right Copper Thickness: 1 Oz vs. 2 Oz.
The decision between 2 oz and 1 oz copper thickness depends on several factors:
Current Requirements: Take into consideration the current carrying capacity of your PCB traces. For higher current applications, copper layers such as 2oz offer more benefits.
Heat Dissipation: Opting for 2 oz copper can help in better thermal management if your design involves components that produce a lot of heat.
Cost Constraints: Budget factors come in. On the plus side, 2 oz copper offers some benefits, though, it is more expensive than 1 oz copper.
Manufacturability: Make sure that your selected copper thickness corresponds to what your PCB manufacturer can produce. Plating and etching are organic operations in the way that the copper clad laminate is dipped into a tank of chemicals for processing. Some of the manufacturers may have restrictions and extra charges for thicker copper layers.
Conclusion
To sum up, the decision of whether to use a 2 oz or 1 oz copper thickness depends on the particular needs of your PCB application. For low to moderate current designs with cost considerations, 1 oz copper is often sufficient. However, for high-current applications demanding robust conductivity, heat dissipation, and durability, 2 oz copper emerges as the preferred choice. By gaining insight into the needs of your project and collaborating with PCB specialists, you will be able to make an educated decision and improve the performance of your PCB design.

